What is Collagen and Why Does it Matter?
Collagen is one of the most abundant and essential proteins in the human body. It gives structure and strength to skin, hair, nails, bones, joints, tendons, and connective tissues. In fact, collagen makes up around 30% of the body’s total protein content.
During youth, our bodies naturally produce sufficient collagen to maintain skin elasticity, strong joints, and overall tissue health. However, after the age of 25–30, natural collagen production begins to decline steadily. This reduction is what leads to visible signs of aging: wrinkles, sagging skin, thinning hair and nails, and joint stiffness or discomfort.
Collagen supplementation has therefore become a cornerstone of modern anti-aging strategies and joint health support. But not all collagen supplements are created equal. The critical question is: which form of collagen truly works?
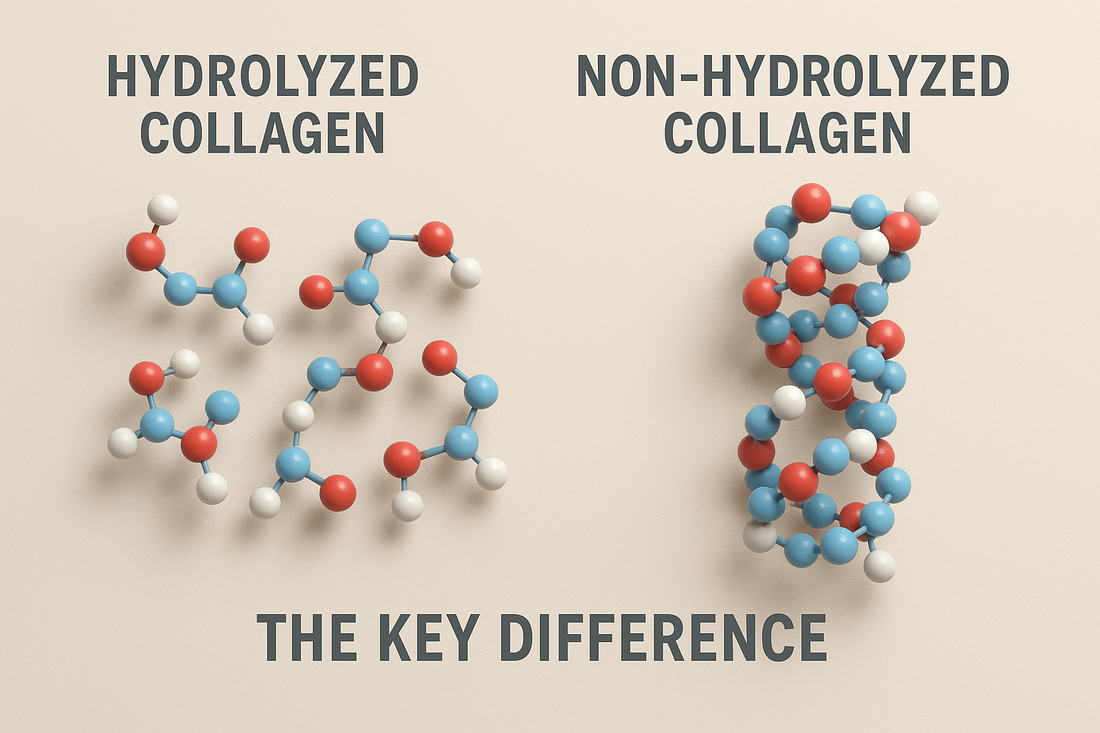
Hydrolyzed vs. Non-Hydrolyzed Collagen – The Key Difference
Collagen supplements can be divided into two major categories: non-hydrolyzed collagen and hydrolyzed collagen (collagen peptides).
Non-Hydrolyzed Collagen
- Large, complex protein molecules that are very difficult for the digestive system to break down.
- Absorption is extremely limited – only a tiny fraction can be used by the body.
- Analogy: it’s like trying to push a whole watermelon through a keyhole – practically impossible.
Hydrolyzed Collagen (Collagen Peptides)
Produced by enzymatic hydrolysis, which breaks collagen down into much smaller peptides.
- These short chains of amino acids easily pass through the intestinal wall and enter the bloodstream.
- Analogy: the watermelon is cut into grapes, which easily slip through the keyhole.
- This process ensures effective collagen absorption and utilization by the body.
Modern science and clinical research consistently show that hydrolyzed collagen is the effective choice.
The Different Types of Hydrolyzed Collagen
While hydrolyzation makes collagen bioavailable, the type of collagen also matters. More than 20 types exist in the body, but three are most important in supplements:
Type I Collagen
- The most abundant type in skin, hair, nails, tendons, and ligaments.
- Essential for skin firmness, elasticity, and reducing the visible signs of aging.
- Hydrolyzed Type I collagen helps maintain youthful skin and strong hair and nails.
Type II Collagen
- Found mainly in cartilage and joints.
- Hydrolyzed Type II collagen has been shown to support mobility, reduce joint pain, and protect cartilage health.
- Particularly important for athletes and individuals with joint conditions.
- Type III Collagen
- Supports blood vessel walls and connective tissue structure.
- Works synergistically with Type I collagen to enhance skin structure and elasticity.
The most advanced supplements combine multiple collagen types to provide comprehensive benefits for beauty, joint health, and tissue regeneration.
Why Hydrolyzed Collagen is Crucial
The difference between hydrolyzed and non-hydrolyzed collagen is not just theoretical – it is measurable.
- Faster absorption: collagen peptides appear in the bloodstream within minutes of ingestion.
- Higher bioavailability: the body can use nearly all of the ingested dose effectively.
- Clinically proven benefits: studies show that daily hydrolyzed collagen intake improves skin hydration, reduces wrinkles, and supports joint health.
Non-hydrolyzed collagen, in contrast, is largely unusable by the body – a supplement form that promises much but delivers little.
Scientific Background – What the Research Says
The benefits of hydrolyzed collagen are well-documented across dermatology, sports medicine, and nutrition research.
- Skin rejuvenation and anti-aging
A systematic review and meta-analysis of 19 clinical studies involving 1,125 participants found that 90 days of oral hydrolyzed collagen significantly improved skin hydration, elasticity, and reduced wrinkles.
- Joint pain and mobility
Randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials show that 10 g of hydrolyzed collagen daily for six months improved cartilage proteoglycan content and reduced knee pain scores in individuals with osteoarthritis.
- Absorption and bioavailability
A 2024 crossover trial demonstrated that after ingestion, hydrolyzed collagen peptides such as Pro-Hyp could be detected in human plasma, proving that the peptides are digested, absorbed, and delivered to tissues.
These studies confirm that hydrolyzed collagen is not only theoretically superior, but clinically effective for both beauty and joint health.
Example of a Modern Collagen Formula
Today’s supplement market is full of collagen products, but not all meet the requirements for real effectiveness. A truly premium formula should:
- Deliver high-dose hydrolyzed collagen (10,000–13,000 mg per serving).
- Contain synergistic ingredients such as hyaluronic acid, NAD+, Pycnogenol, or saw palmetto.
- Include multiple collagen types (I, II, III) for full-spectrum benefits.
One example of such a next-generation formulation is EssenzaVital Liquid Collagen, which combines high-dose hydrolyzed collagen peptides with additional bioactive ingredients for comprehensive anti-aging and wellness support.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
At what age should I start taking collagen?
Collagen production begins to decline around the age of 25–30. Supplementation is particularly recommended from the thirties onward, when visible signs of aging or early joint discomfort often appear.
How much collagen should I take daily?
Research suggests an effective daily dose of 5–13 g of hydrolyzed collagen. Most high-quality liquid formulas provide 10,000–13,000 mg (10–13 g) per serving.
Is liquid collagen better than capsules or powders?
Yes. Liquid hydrolyzed collagen is typically absorbed faster and more efficiently than capsules or powders. The peptides are pre-dissolved and ready for immediate uptake.
How long does it take to see results?
Most people notice improvements in skin hydration and elasticity within 6–8 weeks of consistent use. Joint benefits usually appear after several weeks of daily intake.
What’s the difference between collagen and collagen peptides?
Collagen peptides are the hydrolyzed form of collagen – small chains of amino acids that are easily absorbed and utilized by the body.
Is hydrolyzed collagen safe?
Yes, it is generally safe for healthy adults. Choose products from reputable sources to ensure purity. Pregnant women or people with chronic conditions should consult a doctor first.
Why are extra ingredients like hyaluronic acid or NAD+ important?
Hyaluronic acid enhances skin hydration, NAD+ supports cellular energy and anti-aging processes, Pycnogenol is a powerful antioxidant, and saw palmetto supports men’s health. These additions amplify collagen’s core benefits.
Are all collagens equally effective?
No. Non-hydrolyzed collagen is poorly absorbed and largely ineffective. Hydrolyzed collagen peptides, especially when multiple types are combined, are the only form proven to deliver results.
How can I choose the best collagen supplement?
Look for:
- Hydrolyzed form (collagen peptides)
- High dose (10,000+ mg per serving)
- Multiple collagen types (I, II, III)
- Added synergistic ingredients (hyaluronic acid, NAD+, antioxidants)
Conclusion – The Future of Collagen Supplementation
Collagen supplementation is no longer a passing trend; it has become a science-backed pillar of modern wellness and anti-aging. The hydrolyzed form is the only version proven to be absorbed and used by the body, delivering visible and measurable results for skin, joints, and overall vitality.
The analogy is simple: a watermelon can’t fit through a keyhole, but grapes can. Non-hydrolyzed collagen is the watermelon, hydrolyzed peptides are the grapes.
To achieve the full benefits, it’s also essential to choose the right type – or better yet, a combination of Types I, II, and III – supported by synergistic nutrients.

